In the world of packaging, efficiency, consistency, and speed are crucial. As consumer demand for faster delivery times and higher product quality increases, the need for reliable packaging solutions has never been greater.
Shrink tunnels have emerged as an essential tool for achieving these objectives, particularly when it comes to high-volume shrink wrapping. But what exactly is a shrink tunnel, and why does it matter in packaging?
In this article, we explore the mechanics of shrink tunnels, their benefits, and the factors to consider when incorporating them into a packaging process.
What Is a shrink tunnel?
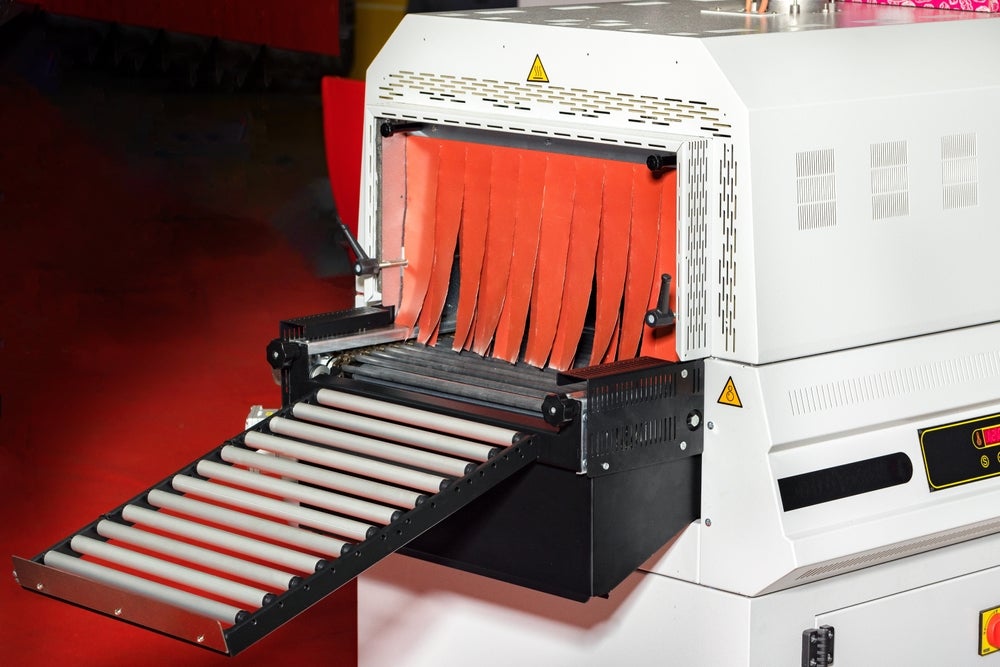
A shrink tunnel is a specialised machine used to apply heat to shrink film, thereby tightly wrapping products in a protective plastic layer.
Typically, the process involves passing items along a conveyor belt through a tunnel, where they are exposed to controlled heat. As the temperature rises, the shrink film contracts, moulding closely to the shape of the item.
These machines come in various types, each designed to suit different packaging needs. The most common types include steam tunnels, which use hot steam to shrink the film; infrared tunnels, which rely on infrared light to generate heat; and recirculating tunnels, which circulate hot air for an even and consistent shrink.
The choice of shrink tunnel depends largely on the type of product, the shrink material being used, and the desired output speed.
For high-volume operations, a shrink tunnel can significantly outperform manual methods such as heat guns or hand-wrapping, saving valuable time and reducing the risk of errors.
Whether you’re wrapping bottles, boxes, or complex shapes, a shrink tunnel offers a fast, consistent, and cost-effective solution.
Advantages of using a shrink tunnel
Consistent and high-quality results
One of the most significant advantages of using a shrink tunnel is the consistency it offers. Manual shrink wrapping with a heat gun can result in uneven shrinkage, leading to defects like wrinkles, holes, or unsightly packaging.
A shrink tunnel, however, ensures that each item is treated under controlled heat, producing uniform results across large production runs. This consistency is especially important in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where product presentation is crucial.
Moreover, the precision of a shrink tunnel reduces the risk of over-heating, which can damage both the product and the packaging.
By adjusting the temperature and conveyor speed, operators can fine-tune the settings to suit the specific material and product size, ensuring a secure and aesthetically pleasing wrap every time.
Speed and efficiency
Time is money, and shrink tunnels excel in speeding up the packaging process. While manual methods can be slow, a shrink tunnel can wrap hundreds or even thousands of products in a fraction of the time.
The conveyor belt allows for continuous operation, with products entering the tunnel, being heated, and exiting automatically in rapid succession. For businesses handling large volumes, this enhanced speed leads to higher throughput and reduced labour costs.
Additionally, shrink tunnels can be integrated into fully automated packaging lines. This integration helps maintain a seamless flow of products through the entire packaging process, from initial wrapping to final distribution. As a result, businesses can meet tight deadlines without compromising on quality.
Enhanced worker satisfaction
In addition to the operational benefits, shrink tunnels also contribute to a better working environment. Unlike heat guns, which require workers to handle and manipulate the product, shrink tunnels automate the process, freeing employees from repetitive tasks.
This not only increases productivity but also reduces the likelihood of workplace injuries caused by prolonged exposure to heat. Employees can focus on monitoring the equipment and ensuring that the process runs smoothly, improving job satisfaction and reducing fatigue.
Considerations when choosing a shrink tunnel
While the advantages of shrink tunnels are clear, selecting the right one for your business requires careful consideration. Here are some factors to keep in mind when choosing a shrink tunnel:
Machine size and capacity
Shrink tunnels vary greatly in size and capacity. Small machines are suited for low to medium-volume operations, while larger models can handle high volumes and larger products.
Businesses must assess their production needs and ensure the shrink tunnel can accommodate the size of the products they intend to wrap. For instance, larger items like furniture or bulk products may require a custom-built tunnel, while smaller consumer goods could be efficiently wrapped in a standard model.
Power consumption
Shrink tunnels require a significant amount of energy, especially larger models with high throughput.
Before purchasing a machine, it is essential to ensure that the facility's power supply can support the machine's energy requirements.
Larger tunnels typically operate on 220V to 480V power, while smaller ones may function on 110V. The power consumption should be balanced with the expected output to optimise cost-effectiveness and minimise energy waste.
Maintenance and operation costs
The initial cost of a shrink tunnel can be high, particularly for advanced models. However, the long-term savings in labour and efficiency often justify the investment. It’s also important to factor in maintenance costs.
Regular servicing and repairs are necessary to keep the equipment running smoothly, and businesses should account for this when budgeting for a shrink tunnel.
When shrink tunnels might not be the best option
While shrink tunnels offer numerous benefits, they may not be the ideal solution for every packaging scenario.
One notable disadvantage is the initial capital investment, which can be prohibitive for small businesses or those with limited budgets. Furthermore, shrink tunnels are generally better suited for high-volume, repetitive packaging tasks.
For smaller-scale or more customised packaging projects, manual methods such as heat guns or shrink chambers might still be preferred due to their lower upfront cost.
Additionally, shrink tunnels require adequate space and proper ventilation. The heat generated during the process can cause an odour, especially during the machine's initial use, and proper airflow is necessary to ensure a safe working environment.
These factors should be considered when evaluating whether a shrink tunnel is the right choice for your operation.
The takeaway
In the competitive world of packaging, shrink tunnels play a vital role in helping businesses meet the demands for speed, consistency, and high-quality packaging.
By automating the shrink-wrapping process, these machines offer a reliable and efficient way to protect products, enhance presentation, and streamline production lines.
However, it is essential to weigh the costs, power requirements, and space considerations before investing in a shrink tunnel. When chosen carefully, these machines can provide significant long-term benefits, positioning businesses for success in an increasingly fast-paced marketplace.